+86 17737144966
Due to its strong adsorption capacity and wide range of applications, activated carbon has occupied an important position in the fields of environmental protection, industry, medicine, etc. However, many companies lack effective means of quality identification when purchasing activated carbon, and often can only rely on the test reports provided by suppliers. Especially in industrial fields such as waste gas and wastewater treatment, since the quality of activated carbon is directly related to the treatment effect, the iodine value of activated carbon is particularly critical. However, some companies only pay attention to the price when purchasing, ignoring the quality of activated carbon, resulting in activated carbon suppliers falsely marking the iodine value to meet the demand for low prices.
In order to help companies better understand the detection methods of activated carbon quality and iodine value, Shufang Activated Carbon will introduce in detail the principles, processes and key control points of detecting the iodine value of activated carbon, in order to enhance the company's ability to distinguish the quality of activated carbon and avoid losses due to false iodine value.
Iodine adsorption value is an important indicator to measure the adsorption capacity of activated carbon and is widely used in standard tests for industrial adsorption. The adsorption capacity of activated carbon for micro-molecule pollutants can be evaluated by iodine adsorption value. Iodine adsorption value refers to the adsorption capacity of activated carbon for iodine under certain conditions, usually expressed as milligrams of iodine adsorbed per gram of activated carbon.
The detection method measures the amount of residual iodine after the activated carbon sample is fully contacted with the iodine solution. By calculating the residual iodine, the iodine adsorption value is determined to evaluate the adsorption performance of activated carbon.
1. Instruments and equipment for detection
The test of iodine adsorption value requires precise instruments and equipment, including:
Balance: Analytical balance with an accuracy of 0.0001g, used to accurately weigh the mass of activated carbon samples and reagents required in the titration process to ensure the accuracy of the test results.
Electric thermostatic oven: Temperature range 0℃ to 300℃, used for pre-treatment drying of activated carbon samples to remove moisture in the samples to avoid affecting the determination of iodine adsorption value.
Pulverizer: Pulverizer with stirring function.
Oscillator: Adjustable frequency and amplitude, used to fully oscillate and adsorb activated carbon samples and iodine standard solution to ensure the uniformity and sufficiency of the adsorption process.
Standard sieve: The sieve opening is below 71 microns (generally 250 mesh standard sieve is used, with a sieve opening of about 66 microns)
2. Reagents used
Several standard reagents are required during the test:
1mol/L iodine standard solution: prepared according to national standards (GB 601) and calibrated with sodium thiosulfate.
0.1mol/L sodium thiosulfate standard solution: prepared according to national standards (GB 601).
Starch indicator: 0.5 g/100 mL, dissolve 0.5 g soluble starch in water, add 90 mL boiling water under stirring, and boil slightly for 2 minutes and cool, and take the supernatant for use.
Hydrochloric acid solution: (1+9) concentration.
3. Sample pretreatment
Before the iodine adsorption value test, the activated carbon sample needs to undergo strict pretreatment steps to ensure the accuracy of the test results:
Dehumidification treatment: For wet activated carbon samples, they need to be dried in a constant temperature environment of 150℃ for 1 hour before crushing.
Crushing: Weigh 10~15g of activated carbon sample and put it into the crusher for 1 minute. Cover the crusher with a towel or plastic bag during the process and open the cover after the dust is dispersed.
Sieve: Pass the crushed sample through a 200-mesh sieve to filter out particles with a particle size of less than 71 microns.
Drying again: Take 5~10g of the sieved sample and place it in a constant temperature box at 150℃ to dry to constant weight.
Step 1: Weigh the sample
Weigh about 0.5g of the crushed and dried activated carbon sample ≤71 microns, put it into a 250mL dry iodine volume bottle, and record the sample weight.
Step 2: Add hydrochloric acid
Add 10.0mL of hydrochloric acid to the volume bottle, shake it slightly to completely wet the activated carbon, and heat it to a slight boil on an electric stove. Then place the sample in a water bath and cool it to room temperature.
Step 3: Add iodine standard solution
Add 50.0mL of 0.1mol/L iodine standard solution to the sample, cover the bottle cap, and oscillate on an oscillator for 15 minutes (vibration frequency is 250~280 times/minute) to ensure that the activated carbon is in full contact with the iodine solution.
Step 4: Filtration
Filter the solution through a single layer of fast filter paper with a diameter of 15cm, and cover the funnel with a glass sheet to prevent iodine from volatilizing. Discard the 10~15mL of filtrate before the filter paper, and only collect the subsequent filtrate.
Step 5: Titrate the filtrate
Take 10.0 mL of the filtrate, place it in 100 mL of distilled water, and titrate it with 0.1 mol/L sodium thiosulfate solution until it turns light yellow. Then add 2 mL of starch indicator and continue titrating until it turns colorless. Record the volume of sodium thiosulfate consumed.
Calculation of results
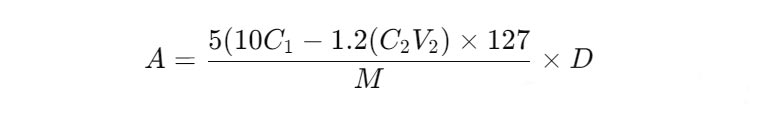
A: iodine adsorption value of the sample, mg/g;
C1: concentration of iodine standard solution, mol/L;
C2: concentration of sodium thiosulfate solution, mol/L;
V2: volume consumed by sodium thiosulfate solution, mL;
M: sample weight, g;
D: correction factor.
In the detection of iodine adsorption value, the accuracy requirement is high. Usually, the difference in iodine adsorption value of more than two parallel samples should be controlled within 5%.
Key points in the detection process
Control the size of activated carbon particles and shaking time: The smaller the activated carbon particles, the larger its specific surface area and the stronger its adsorption capacity. The particle size of the sample must be strictly controlled to ≤71 microns, and the oscillation time and frequency must be accurate.
Sample drying treatment: Because activated carbon has strong hygroscopicity, excessive moisture will significantly affect the weighing accuracy. Therefore, drying treatment is very necessary.
Rapid weighing: Activated carbon has strong water absorption capacity, and long exposure to air will lead to inaccurate weighing, so using the reduction method to weigh can reduce errors.
Avoid iodine volatilization: Iodine is easy to volatilize, so the iodine standard solution needs to be added along the bottle wall and a well-sealed volumetric bottle should be selected to reduce iodine loss.
Filter paper selection: Filter paper has a greater adsorption effect on iodine, so fast filter paper should be used, and the first 10mL of filtrate should be discarded to ensure the accuracy of the filtrate.
Adjust weighing: According to the different iodine values of the sample, adjust the sample weighing range to ensure that the titration is within the appropriate range. When the iodine value is low, the sample volume should be increased accordingly.
Significance and application of test results
The test results of iodine adsorption value are of great significance to the application of activated carbon. The higher the iodine value, the more developed the microporous structure of activated carbon and the stronger the adsorption capacity, so it has more application advantages in industrial waste gas, water purification and other fields. Through the test of iodine adsorption value, users can choose the appropriate type of activated carbon according to actual needs to achieve better treatment effect.